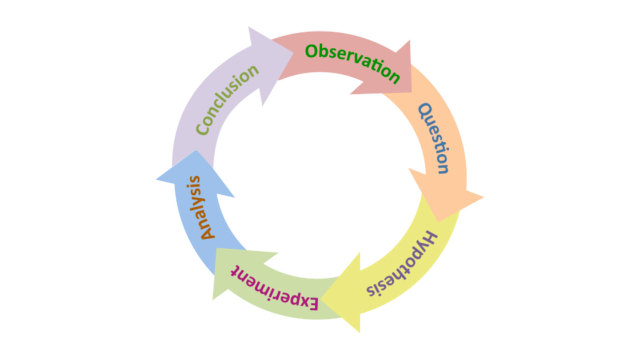
The scientific method is an empirical method of acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. It involves careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, given that cognitive assumptions can distort how one interprets the observation. It involves formulating hypotheses, via induction, based on such observations; experimental and measurement-based testing of deductions drawn from the hypotheses; and refinement (or elimination) of the hypotheses based on the experimental findings. These are principles of the scientific method, as distinguished from a definitive series of steps applicable to all scientific enterprises.
Though diverse models for the scientific method are available, there is in general a continuous process that includes observations about the natural world. People are naturally inquisitive, so they often come up with questions about things they see or hear, and they often develop ideas or hypotheses about why things are the way they are. The best hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested in various ways. The most conclusive testing of hypotheses comes from reasoning based on carefully controlled experimental data. Depending on how well additional tests match the predictions, the original hypothesis may require refinement, alteration, expansion or even rejection. If a particular hypothesis becomes very well supported, a general theory may be developed.
Although procedures vary from one field of inquiry to another, they are frequently the same from one to another. The process of the scientific method involves making conjectures, deriving predictions from them as logical consequences, and then carrying out experiments or empirical observations based on those predictions. A hypothesis is a conjecture, based on knowledge obtained while seeking answers to the question. The hypothesis might be very specific, or it might be broad. Scientists then test hypotheses by conducting experiments or studies. A scientific hypothesis must be falsifiable, implying that it is possible to identify a possible outcome of an experiment or observation that conflicts with predictions deduced from the hypothesis; otherwise, the hypothesis cannot be meaningfully tested.